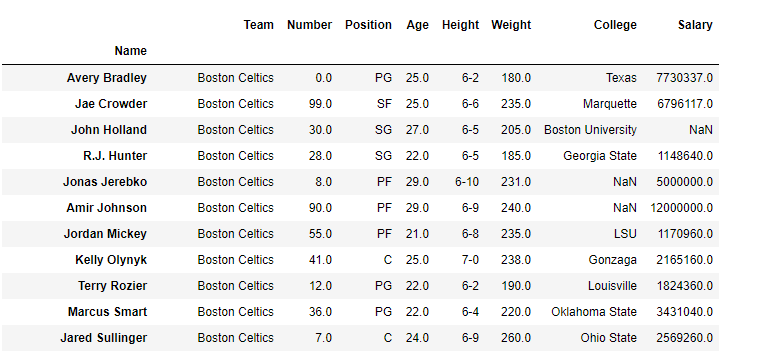
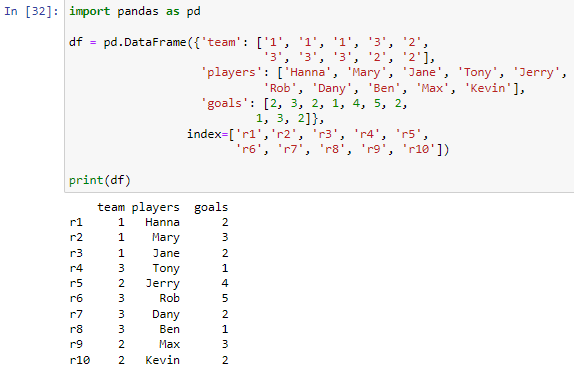
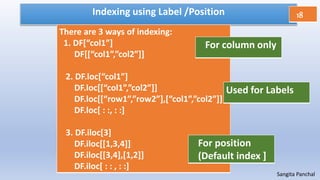
41 indexing using labels in dataframe
Python | Pandas Extracting rows using .loc[] - GeeksforGeeks 30.09.2019 · Output: As shown in the output image, All rows with team name “Utah Jazz” were returned in the form of a data frame. Example #4: Extracting rows between two index labels In this example, two index label of rows are passed and all the rows that fall between those two index label have been returned (Both index labels Inclusive). MultiIndex / advanced indexing — pandas 1.5.0 documentation A MultiIndex can be created from a list of arrays (using MultiIndex.from_arrays()), an array of tuples (using MultiIndex.from_tuples()), a crossed set of iterables (using MultiIndex.from_product()), or a DataFrame (using MultiIndex.from_frame()). The Index constructor will attempt to return a MultiIndex when it is passed a list of tuples. The ...
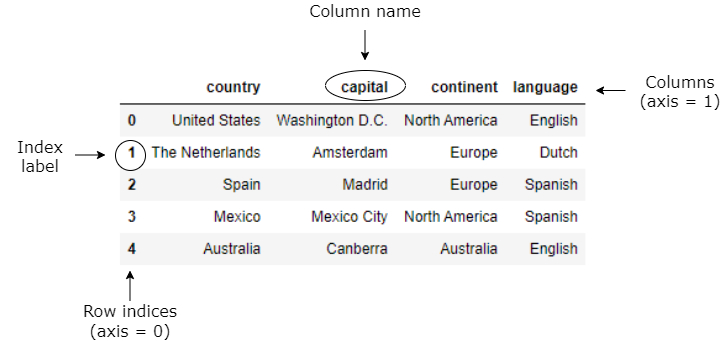
Indexing and selecting data — pandas 1.5.0 documentation Indexing and selecting data# The axis labeling information in pandas objects serves many purposes: Identifies data (i.e. provides metadata) using known indicators, important for analysis, visualization, and interactive console display. Enables automatic and explicit data alignment. Allows intuitive getting and setting of subsets of the data set.

Indexing using labels in dataframe
pandas.DataFrame.lookup — pandas 1.5.0 documentation Deprecated since version 1.2.0: DataFrame.lookup is deprecated, use pandas.factorize and NumPy indexing instead. For further details see Looking up values by index/column labels . Given equal-length arrays of row and column labels, return an array of the values corresponding to each (row, col) pair. MultiIndex / advanced indexing — pandas 1.5.0 documentation A MultiIndex can be created from a list of arrays (using MultiIndex.from_arrays()), an array of tuples (using MultiIndex.from_tuples()), a crossed set of iterables (using MultiIndex.from_product()), or a DataFrame (using MultiIndex.from_frame()). The Index constructor will attempt to return a MultiIndex when it is passed a list of tuples. The ... Indexing, Slicing and Subsetting DataFrames in Python Indexing by labels loc differs from indexing by integers iloc. With loc, both the start bound and the stop bound are inclusive. When using loc, integers can be used, but the integers refer to the index label and not the position. For example, using loc and select 1:4 will get a different result than using iloc to select rows 1:4.
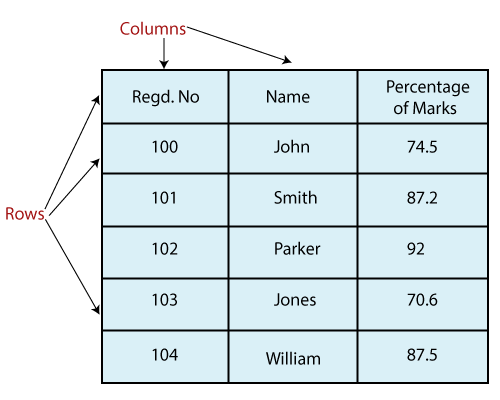
Indexing using labels in dataframe. DataFrame — pandas 1.5.0 documentation Get the 'info axis' (see Indexing for more). DataFrame.iterrows Iterate over DataFrame rows as (index, Series) pairs. DataFrame.itertuples ([index, name]) Iterate over DataFrame rows as namedtuples. DataFrame.lookup (row_labels, col_labels) (DEPRECATED) Label-based "fancy indexing" function for DataFrame. DataFrame.pop (item) Python | Pandas DataFrame - GeeksforGeeks 10.01.2019 · Pandas DataFrame is two-dimensional size-mutable, potentially heterogeneous tabular data structure with labeled axes (rows and columns). A Data frame is a two-dimensional data structure, i.e., data is aligned in a tabular fashion in rows and columns. Pandas DataFrame consists of three principal components, the data, rows, and columns.. We will get a brief insight … DataFrame — PySpark 3.3.0 documentation - Apache Spark DataFrame.add_prefix (prefix) Prefix labels with string prefix. DataFrame.add_suffix (suffix) Suffix labels with string suffix. DataFrame.align (other[, join, axis, copy]) Align two objects on their axes with the specified join method. DataFrame.at_time (time[, asof, axis]) Select values at particular time of day (example: 9:30AM). Indexing and selecting data — pandas 1.5.0 documentation Indexing and selecting data# The axis labeling information in pandas objects serves many purposes: Identifies data (i.e. provides metadata) using known indicators, important for analysis, visualization, and interactive console display. Enables automatic and explicit data alignment. Allows intuitive getting and setting of subsets of the data set.
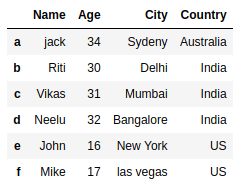
Indexing, Slicing and Subsetting DataFrames in Python Indexing by labels loc differs from indexing by integers iloc. With loc, both the start bound and the stop bound are inclusive. When using loc, integers can be used, but the integers refer to the index label and not the position. For example, using loc and select 1:4 will get a different result than using iloc to select rows 1:4. MultiIndex / advanced indexing — pandas 1.5.0 documentation A MultiIndex can be created from a list of arrays (using MultiIndex.from_arrays()), an array of tuples (using MultiIndex.from_tuples()), a crossed set of iterables (using MultiIndex.from_product()), or a DataFrame (using MultiIndex.from_frame()). The Index constructor will attempt to return a MultiIndex when it is passed a list of tuples. The ... pandas.DataFrame.lookup — pandas 1.5.0 documentation Deprecated since version 1.2.0: DataFrame.lookup is deprecated, use pandas.factorize and NumPy indexing instead. For further details see Looking up values by index/column labels . Given equal-length arrays of row and column labels, return an array of the values corresponding to each (row, col) pair.



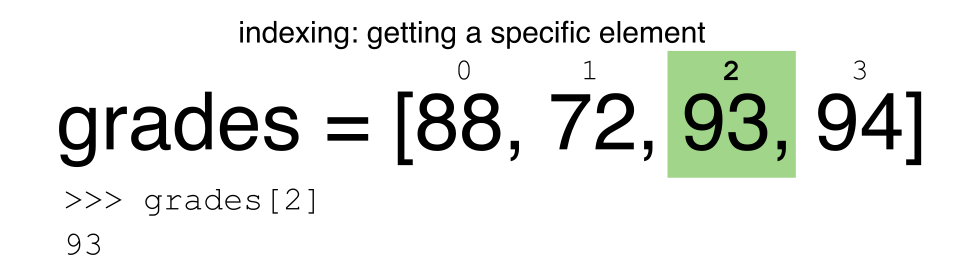

-Feb-14-2022-02-23-55-63-PM.png?width=650&name=Pandas%20Indexing%20(V4)-Feb-14-2022-02-23-55-63-PM.png)


















Post a Comment for "41 indexing using labels in dataframe"